A pharmaceutical manufacturer, a construction firm owner, and a chemical processor all walk into a bar… What do they have in common? It should be that they all understand what the waste hierarchy is, and how to apply it.
Regardless of your industry or job role, if your business generates hazardous waste, understanding and applying the waste hierarchy is essential. It’s a powerful framework for reducing environmental impact, cutting costs, and improving operational efficiency.
Let’s remove the guesswork from the waste hierarchy to help you understand what it is, why it matters, and how you can use it to benefit your business.
- What Is the Waste Hierarchy?
- The Waste Hierarchy Pyramid Explained
- Why Is the Waste Hierarchy Important for UK Businesses?
- Common Challenges (and How to Overcome Them)
- How to Implement the Waste Hierarchy in Your Business
- Myths About the Waste Hierarchy
- Final Thoughts: Why Hazport?
What Is the Waste Hierarchy?
The waste hierarchy is a structured approach to waste management that ranks options from most to least environmentally preferable. It’s designed to help businesses make smarter decisions about how they handle waste – especially hazardous waste – by prioritising prevention and minimising reliance on landfill.
The waste hierarchy is embedded in UK law through the Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2011, which require businesses to apply this framework when managing waste.
But it’s more than just another legal framework to add to the list of burdens when managing waste. Applying the waste hierarchy is beneficial for your business, your staff, and the planet, helping you manage your waste in the most effective and sustainable way.
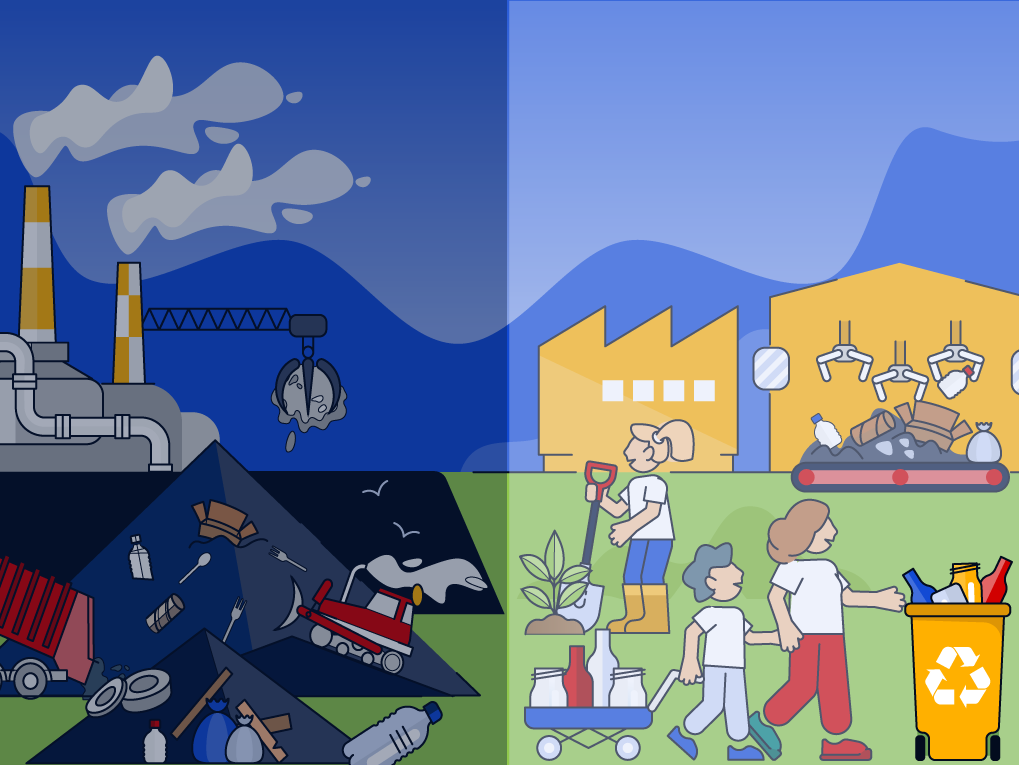
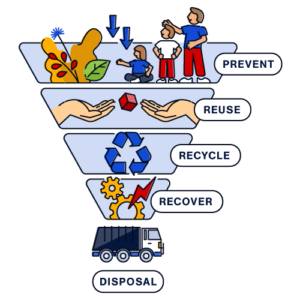
The Waste Hierarchy Pyramid Explained
The waste hierarchy is often visualised as an inverted pyramid with seven levels beginning with the most sustainable solution and ending with the least environmentally favourable.
Let’s take a more detailed look at each level of the waste hierarchy pyramid:
#1 Prevent: Only use what you need to use.
Goal: Avoid generating waste in the first place (easy, right?)
This is the most effective and sustainable option. Examples:
- Redesigning processes to eliminate unnecessary materials.
- Switching to digital documentation to reduce paper use.
- Choosing less hazardous substances in production.
Why it matters: Prevention eliminates the need for waste handling altogether, reducing environmental impact and operational costs.
#2 Reuse: Use it again and again. And again.
Goal: Extend the life of products and materials before they become waste.
Examples:
- Reusing chemical containers or pallets.
- Refurbishing equipment or tools.
- Repurposing offcuts or surplus materials.
Why it matters: Reuse reduces demand for new resources and diverts waste from disposal routes.
#3 Recycle: Can it become something else?
Goal: Convert waste into new materials or products.
Examples:
- Recycling metal, plastic, or cardboard packaging.
- Using specialist services to recycle contaminated PPE or lab containers.
Why it matters: Recycling supports the circular economy, but it still consumes energy, this is why is less favourable than prevention and reuse.
#4 Recover: Transform it into energy.
Goal: Extract value from waste, typically through energy generation.
Examples:
- Incinerating non-recyclable waste to produce electricity or heat.
- Using anaerobic digestion for biodegradable industrial waste.
Why it matters: Recovery is preferable to disposal because it captures some value from waste that can’t be reused or recycled.
#5 Disposal: There’s no coming back.
Goal: Safely and legally dispose of waste that cannot be otherwise managed.
This is the least sustainable option and should always be the last resort. Examples:
- Landfilling hazardous residues.
- High-temperature incineration without energy recovery.
Why it matters: Disposal is the last resort due to its environmental impact and cost. It must be done in full compliance with UK regulations.
Why Is the Waste Hierarchy Important for UK Businesses?
To expand on what we mentioned earlier about the waste hierarchy being more than just another legal framework to adhere to, here are some of the benefits you can enjoy by doing so.
Legal Compliance
Let’s begin with the compliance aspect… UK law requires businesses to apply the waste hierarchy and take every reasonable step to apply it as a priority order. It’s worth noting that a business may depart from the priority order to achieve the best overall environmental outcome where justified by lifecycle thinking.
In short, if you just apply it in priority order to your waste production, you can’t go wrong.
 Cost Savings
Cost Savings
Reducing waste at the source of production lowers disposal costs and can also reduce your procurement spend. For example, reusing containers or buying what you need in bulk can cut both waste and costs.
Environmental Responsibility
Needless to say – actually, we’ll say it anyway – hazardous waste can have serious environmental consequences. Applying the waste hierarchy helps reduce pollution, conserve resources and support sustainability goals.
Reputation and ESG
Customers, partners, investors and regulators increasingly expect businesses to demonstrate environmental responsibility. Following the waste hierarchy supports your Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) credentials.
Operational Efficiency
Streamlining waste processes and applying the waste hierarchy can improve site safety, reduce clutter and enhance productivity across your teams.
Common Challenges (and How to Overcome Them)
As with the application of any framework or process, the waste hierarchy may present some challenges that feel unique to your business but you’ll be surprised how common some of these are.
Here are the most common challenges along with some practical solutions:
Challenge: Lack of awareness or training
- Solution: Many employees are unaware of the waste hierarchy or how to apply it. Regular training, clear signage and internal campaigns can build a culture of compliance and sustainability.
Challenge: Complex or mixed waste streams
- Solution: Hazardous waste often includes mixed materials that are difficult to separate. Conducting a professional waste audit and working with a specialist like Hazport can help identity and streamline segregation.
Challenge: Limited on-site space for segregation
- Solution: Businesses with limited space may struggle to store multiple waste types. Use compact, clearly labelled containers and schedule frequent collections to manage space efficiently.
Challenge: Uncertainty around legal obligations
- Solution: Regulations can be complex and change over time. Partnering with a licensed waste management provider that provides the care and attention to detail you deserve ensures your business stays compliant and up to date.
Challenge: Perceived cost of sustainable practices
- Solution: Some businesses assume that prevention, reuse, or recycling is more expensive. In reality, these practices often reduce procurement and disposal costs over time – especially when waste is minimised at source.
How to Implement the Waste Hierarchy in Your Business
The waste hierarchy can easily be implemented into your business in five simple steps, followed by ongoing monitoring and reviewing for improvement.
Step One: Conduct a waste audit
- Identify what types of waste you produce, how much of it, and from where.
- Highlight opportunities for reduction, reuse, or recycling.
Step Two: Develop a waste management plan
- Set clear goals that align with the waste hierarchy.
- Assign responsibilities and review progress regularly.
 Step Three: Train your teams
Step Three: Train your teams
- Ensure everyone understands how to correctly segregate and handle waste.
- Use signage, colour coding, and regular refreshers.
Step Four: Choose the right waste partner
- Work with a licensed provider like Hazport who understands your industry and its nuances and can help you stay compliant.
Step Five: Review your procurement practices
- Choose reusable over recyclable materials.
- Avoid over-ordering or unnecessary packaging.
Ongoing Step: Monitor and improve
- Track your waste volumes and costs over time.
- Celebrate successes and refine your approach over time.
 Myths About the Waste Hierarchy
Myths About the Waste Hierarchy
Have you noticed there seems to be myths and conspiracies about everything these days…
“It’s only for recycling.”
False. Recycling is just one step, and it’s not even the most favourable – prevention and reuse come first.
“It doesn’t apply to hazardous waste.”
False. The waste hierarchy is especially important for hazardous waste due to its inherent risks.
“It’s too expensive to implement and follow.”
False. Prevention and reuse often save money in the long run.
Final Thoughts: Why Hazport?
At Hazport, we specialise in helping UK businesses manage hazardous waste safely, sustainably, and in full compliance with regulations, including frameworks like the waste hierarchy. Whether you need a waste audit, compliant disposal, or help training your team, we’re here to support you.
Ready to remove the guesswork and take control of your hazardous waste?
Contact us today to learn more about our hazardous waste services and how we can help your business reduce hazardous waste and manage the waste you generate more effectively.