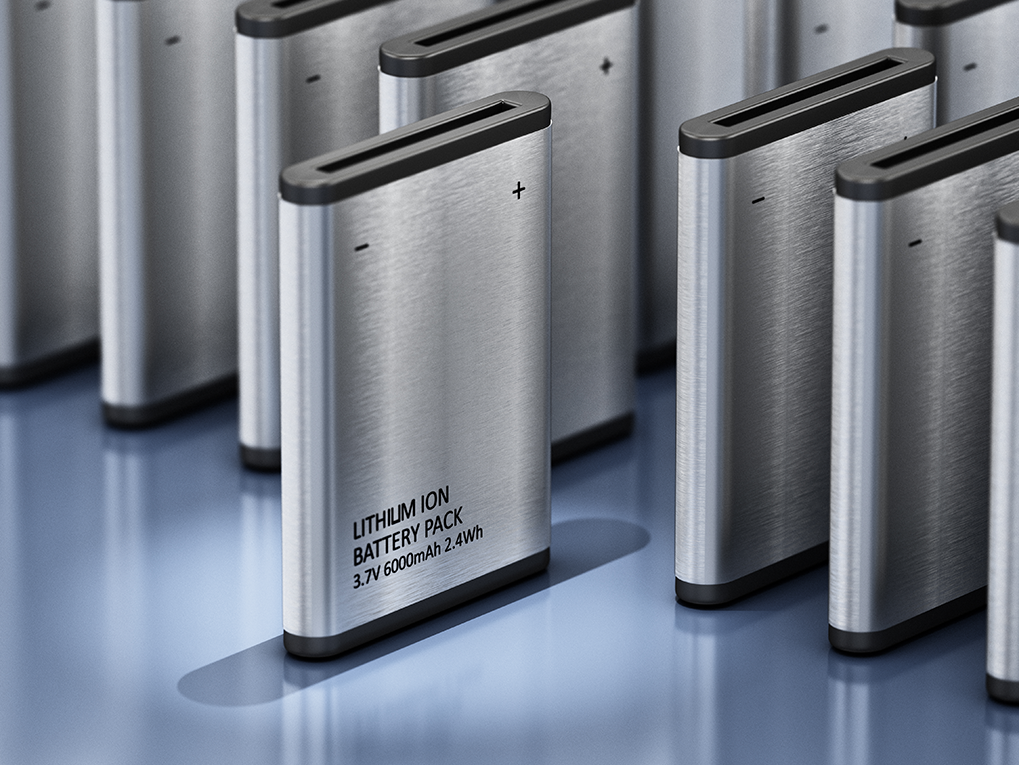
Ever tossed a lithium battery away without giving it a second thought? You could be an unintentional firestarter.
Research shows that 54% of businesses have experienced incidents linked to lithium batteries, with one in five reporting fires or explosions. And with these batteries powering everything from laptops and handheld scanners to cordless tools and UPS modules, there’s no avoiding them in the workplace.
They’re compact, convenient and powerful – but when end of life or become damaged, they stop being a benefit and start becoming a risk.
This guide removes the guesswork and strips away the jargon to explain, in plain language, how UK businesses can manage lithium battery disposal safely, legally, and confidently – keeping your workforce protected and your workplace compliant.
- What Is a Lithium Battery?
- Where You’ll Find Lithium Battery Waste in the Workplace
- What’s the Business Risk of Incorrect Disposal?
- 6 Steps for Compliant Lithium Battery Disposal
- The Dos and Don’ts of Lithium Battery Disposal
- How to Respond to a Lithium Battery Fire
- Recycling Routes for Lithium Batteries
- Remove the Guesswork with Hazport
What Is a Lithium Battery?
‘Lithium battery’ is the umbrella term for batteries that use lithium chemistry to store energy. Under that umbrella sit two main types:
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) – the rechargeable subset, powering most modern technology and tools.
- Lithium metal (primary) – non-rechargeable cells such as many button or coin batteries.
Why so widespread? Lithium is the lightest metal on the periodic table, meaning these batteries deliver high energy density whilst remaining compact and portable – a perfect match for modern devices and equipment.
Where You’ll Find Lithium Batteries in the Workplace
 Lithium-ion (rechargeable):
Lithium-ion (rechargeable):
- IT equipment – laptops, mobiles, tablets, power banks.
- Warehouse/production – barcode scanners, handheld terminals, robotics such as AMRs and AGVs.
- Facilities/critical power – UPS modules, server room backups, energy storage.
- Tools and equipment – cordless drills, saws, grounds maintenance kit.
- Fleet/mobility – e-bikes, e-scooters, e-cargo bikes.
- R&D – prototype cells, packs and modules.
 Lithium metal (non-rechargeable)
Lithium metal (non-rechargeable)
- Office/tech – coin cells in keyboards, mice, access fobs.
- Safety and security – sensors, detectors, specialist cameras.
- Industrial/lab – data loggers, instrumentation, metering devices.
It’s a good idea to create a simple internal register – what you have, where it’s stored, who’s responsible, and its condition. This is one of the easiest ways to improve safety and compliance across your site.
Need help creating a one? Our team can support you.
 What’s the Business Risk Incorrect Disposal?
What’s the Business Risk Incorrect Disposal?
As we noted at the outset, 54% of businesses have experienced a lithium battery-related incident – this shows that lithium batteries bring real business-critical risks when mishandled:
Thermal runaway
Physical damage, overcharging, or internal faults can trigger rapid self-heating, venting, the release of toxic gases, and ignition.
Hidden hazards
‘Dead’ batteries can still hold a charge; unsuitable storage can lead to short circuits; poor packaging can ignite in transit.
Regulatory exposure
Lithium batteries fall into hazardous waste controls, ADR (transport of dangerous goods), and battery/WEEE producer responsibility rules. Getting it wrong risks fires, fines and reputational damage.
The answer isn’t panic – it’s good housekeeping and competent partners.
6 Steps for Compliant Lithium Battery Disposal
#1 Identify and Classify
- Record chemistry: Lithium-ion or lithium metal.
- Note form: Loose cells/modules/packs or embedded in equipment.
- Check condition: Intact or damaged/defective.
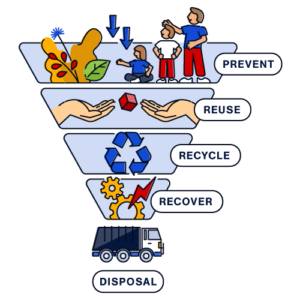 #2 Apply the Waste Hierarchy
#2 Apply the Waste Hierarchy
- Prevent: Avoid over-ordering, monitor battery health and rotate stock.
- Reuse/repurpose: Consider manufacturer take-back schemes and second-life options.
- Recycle: Prioritise routes that maximise resource recovery. Disposal should always be the last resort.
See our blog on the waste hierarchy to learn more.
#3 Package and Store Safely
- Li-ion: Tape terminals, add inert cushioning and segregate suspect units.
- Lithium metal: Keep dry, avoid water exposure and keep separate.
- All damaged units: Isolate and await specialist overpacking.
 #4 Choose a Licensed Waste Partner
#4 Choose a Licensed Waste Partner
Expect:
- Waste carrier license.
- ADR capability.
- Evidence of authorised downstream facilities.
- Clear, straight-talking advice and fast turnaround.
That’s the Hazport standard!
 #5 Move Under ADR with Correct Paperwork
#5 Move Under ADR with Correct Paperwork
Your waste partner should manage:
- UN numbers.
- ADR labels.
- Waste transfer/consignment notes.
- Specialist provisions for packaging and transport.
#6 Verify Treatment and Close the Loop
Keep recovery documentation for:
- ESG reporting.
- Environmental audits.
- Compliance evidence.
Damaged Lithium Battery Disposal (High-Risk Scenario)
Treat any of the following as a serious red flag:
- Swelling
- Hissing
- Scorch marks
- Electrolyte smell
- Water damage
- Stop and isolate. Move the item (if safe) into a fire-resistant quarantine container, away from people and combustibles.
- No DIY Don’t try to open, flatten, cool with improvised methods, or try to charge, test, or disconnect cells.
- Call a specialist. Damaged/defective lithium batteries require special handling and UN-spec packaging for transport; they must be moved by trained personnel with the right materials and documentation.
- Record the incident. Note where it came from and how it was found – this helps with safe consignment and future prevention, as well as supporting classification and documentation.
The result? A protected workforce, a safer workplace, compliant paperwork, and a clean and simple handover to an approved facility. No drama. No guesswork.
The Dos and Don’ts of Lithium Battery Disposal
Let’s start with the umbrella rules: Never open one inside a building… (just checking you’re still with us).
Do:
- Keep Li-ion and lithium metal separate, as well as intact vs damaged units.
- Use non-conductive, fire-resistant, lidded containers with inert cushioning.
- Tape exposed terminals on loose cells and small packs.
- Store cool and dry, away from heat, sunlight and pressure.
- Label clearly and maintain an up-to-date inventory.
- When unsure: stop, isolate and escalate to a specialist.
Don’t:
- Don’t crush, puncture or dismantle packs – no DIY ‘battery surgery’.
- Don’t mix batteries with WEEE, cardboard, metals or combustibles.
- Don’t ‘test’ damaged batteries by charging them.
- Don’t improvise packaging – ADR rules aren’t optional.
- Don’t move damaged/defective units without specialist UN-approved overpacking and paperwork.
Type-Specific Notes:
Lithium-ion (rechargeable subset)
- Biggest risk: Thermal runaway.
- Damaged Li-ion must be packed and shipped under special ADR provisions.
Lithium metal (non-rechargeable)
- Water-reactive – Keep dry and away from moisture.
- Prevent short circuits with proper terminal protection and separation.
One thing to remember:
If it’s damaged, unknown or making you nervous – stop and isolate. Call a specialist to classify and package your lithium battery waste.
 How to Respond to a Lithium Battery Fire
How to Respond to a Lithium Battery Fire
Knowing how to handle hazardous waste in an emergency is crucial for any business that produces or uses hazardous materials.
Always put people before property. If there’s smoke, flames, popping, or toxic vapour: evacuate the area, raise the alarm, and call 999.
For a lithium-ion battery fire: if it’s safe to attempt first-aid firefighting and you’re trained to do so, cool aggressively with water from a distance to stop thermal runaway spreading. Water helps remove heat even if flames reappear. A CO2 or foam extinguisher may knock down the flames, but cooling is critical to prevent re-ignition.
For lithium metal battery fires: DO NOT USE WATER. Use a Class D (metal fire) agent in line with your fire strategy and training.
For large packs (e-bikes, UPS, energy storage systems): Isolate, evacuate and let the fire service handle it. They may apply large volumes of water for extended cooling.
Prevention always beats firefighting: Correct storage, separation, isolation of suspect units and early action dramatically reduce incidents before they start. That’s the waste hierarchy mindset – prevention first.
Recycling Routes for Lithium Batteries
Moving a little further down the waste hierarchy now to recycling, there are options for lithium batteries. A common question we hear is “How much of a lithium battery can be recycled?”
There isn’t a single percentage for every battery, because chemistry, design and condition vary. But as a general rule of thumb:
- Metals such as copper, aluminium, nickel and cobalt are routinely recovered.
- Lithium recovery is increasing as UK/EU capacity grows.
- Plastics and electrolytes may be partially recovered.
- Lithium metal cells follow more specialised routes.
What matters is traceability. When batteries are consigned to authorised treatment, you can evidence recovery through completion certificates and downstream audit trails.
That raises another critical question…
 Who’s Allowed to Recycle Lithium Batteries?
Who’s Allowed to Recycle Lithium Batteries?
As per hazardous waste regulations, only authorised facilities can treat lithium batteries in the UK, and routes depend on whether the battery is standalone or embedded in WEEE equipment. Here’s an overview:
- Standalone batteries: Approved Battery Treatment/Export Operators (ABTO/ABEO) handle sorting, discharge, disassembly and materials recovery.
- Batteries in WEEE: Approved Authorised Treatment Facilities (AATFs) depollute the equipment first, then route batteries for specialist processing.
- Interim/bulking transfer: Permitted hazardous waste transfer stations may consolidate and prepare consignments before final treatment.
It’s your responsibility to consign to licensed carriers and permitted sites, with the correct waste codes and ADR details. It’s your waste partner’s job to get it right, end-to-end, and keep your documentation audit-ready and compliant.
 Remove the Guesswork with Hazport
Remove the Guesswork with Hazport
At Hazport, remove the guesswork from hazardous waste and make disposal easy. Our mobile chemists, fast response times, ADR-compliant packaging, and end-to-end traceability through approved facilities make us a good choice as a partner for your business.
No more waiting, guessing or wondering – just safe, compliant outcomes that stand up to scrutiny and make your audits pain-free.
Our experienced team is ready to support you every step of the way, from identifying and segregating waste to final disposal.
Contact us today to learn more about our WEEE waste disposal services and how we can help you create a safer and more compliant waste management system for your facility.



 Imagine you’re halfway through another normal workday, and someone knocks over a container – as the smell of chemicals hits the air, the panic sets in. What happens now?
Imagine you’re halfway through another normal workday, and someone knocks over a container – as the smell of chemicals hits the air, the panic sets in. What happens now? What Is Chemical Spill Safety?
What Is Chemical Spill Safety? Serious harm to health – Exposure to certain chemicals can lead to burns, breathing problems, or even long-term conditions like cancer. Some gases are toxic in tiny amounts. Others can ignite with the slightest spark.
Serious harm to health – Exposure to certain chemicals can lead to burns, breathing problems, or even long-term conditions like cancer. Some gases are toxic in tiny amounts. Others can ignite with the slightest spark. Pillar I: Spill Prevention
Pillar I: Spill Prevention Pillar II: Spill Control and Containment
Pillar II: Spill Control and Containment Pillar III: Spill Cleanup
Pillar III: Spill Cleanup Pillar IV: Report and Review
Pillar IV: Report and Review The Hierarchy of Spill Management
The Hierarchy of Spill Management Ultimately, the responsibility for a chemical spill lies with you, the waste producer. Under the UK hazardous waste laws and regulations, you’re required to ensure that any spill is managed safely and that the resulting waste is classified, labelled and
Ultimately, the responsibility for a chemical spill lies with you, the waste producer. Under the UK hazardous waste laws and regulations, you’re required to ensure that any spill is managed safely and that the resulting waste is classified, labelled and 
 What Is the Waste Duty of Care
What Is the Waste Duty of Care #1 Classify Your Waste Correctly
#1 Classify Your Waste Correctly #2 Store Your Waste Safely
#2 Store Your Waste Safely


 Shropshire has come a long way from being known only as rural farmland and market towns, and it’s still living up to its reputation of being the birthplace of the industrial revolution. In fact, the region is seeing steady growth in several key industrial sectors, particularly:
Shropshire has come a long way from being known only as rural farmland and market towns, and it’s still living up to its reputation of being the birthplace of the industrial revolution. In fact, the region is seeing steady growth in several key industrial sectors, particularly:
 Conducting Waste Audits
Conducting Waste Audits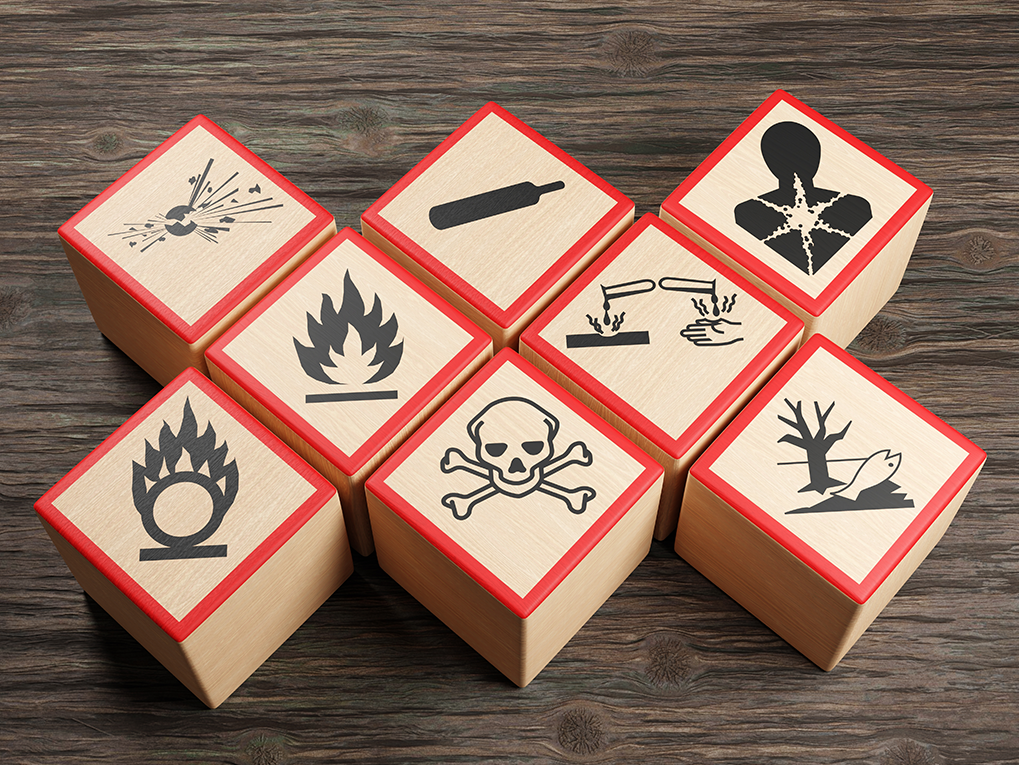












 Practical Tips for Hazardous Waste Compliance
Practical Tips for Hazardous Waste Compliance

 Common types of chemical wastes include:
Common types of chemical wastes include:
 It’s essential to outline a plan for hazardous waste emergencies so that you’re prepared when they happen. Sudden hazardous waste emergencies can pose a risk to health and the environment due to their toxic effects and potential exposure to hazardous chemicals.
It’s essential to outline a plan for hazardous waste emergencies so that you’re prepared when they happen. Sudden hazardous waste emergencies can pose a risk to health and the environment due to their toxic effects and potential exposure to hazardous chemicals. The safety of everyone in the surrounding area in case of a hazardous waste emergency is paramount. The evacuation plan is initiated by sounding the emergency alert. This leads people to their designated safe places or assembly points, away from the hazardous waste. Your occupational safety plan must also include individuals with disabilities and detailed routes that avoid the affected area.
The safety of everyone in the surrounding area in case of a hazardous waste emergency is paramount. The evacuation plan is initiated by sounding the emergency alert. This leads people to their designated safe places or assembly points, away from the hazardous waste. Your occupational safety plan must also include individuals with disabilities and detailed routes that avoid the affected area. Once you’ve contained the spill, your focus needs to shift towards stopping any further contamination to the environment.
Once you’ve contained the spill, your focus needs to shift towards stopping any further contamination to the environment.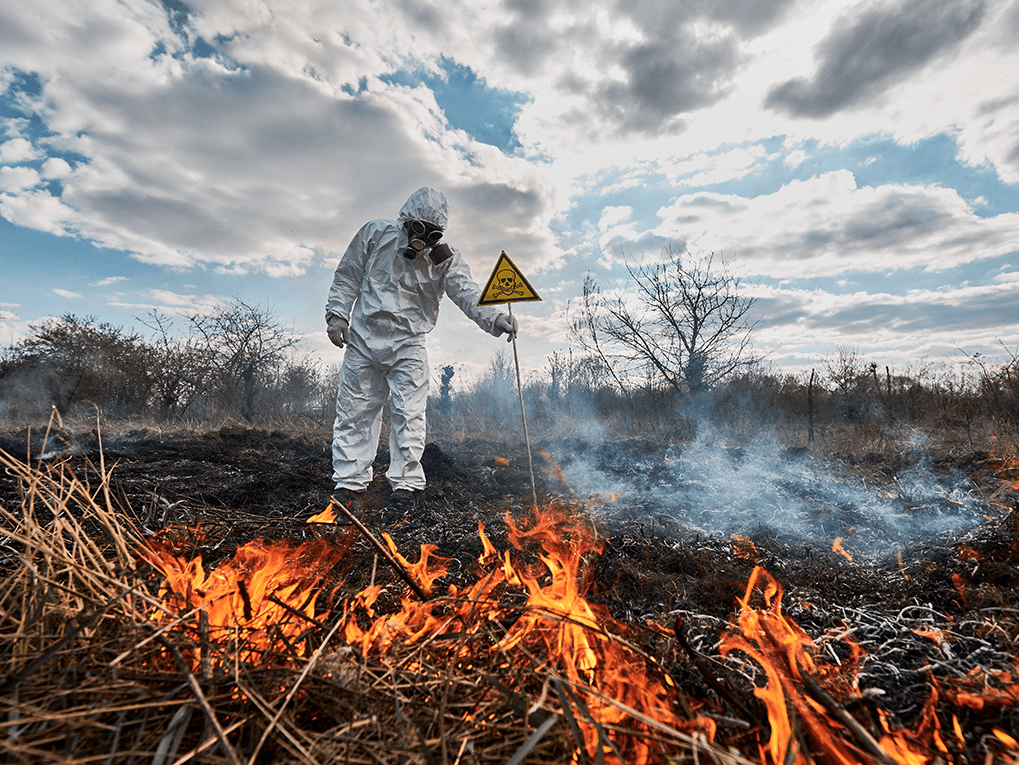

 Soil contamination is another significant consequence of hazardous waste mismanagement. Heavy metals, chemical waste spills, and agricultural runoff deposit harmful substances in the soil. These substances can remain in the soil for years, eventually altering the soil’s composition and fertility. This degradation impacts plant growth and crop yields, decreasing biodiversity and disrupting soil health.
Soil contamination is another significant consequence of hazardous waste mismanagement. Heavy metals, chemical waste spills, and agricultural runoff deposit harmful substances in the soil. These substances can remain in the soil for years, eventually altering the soil’s composition and fertility. This degradation impacts plant growth and crop yields, decreasing biodiversity and disrupting soil health.
